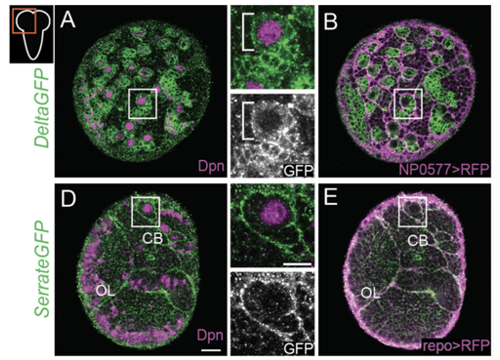
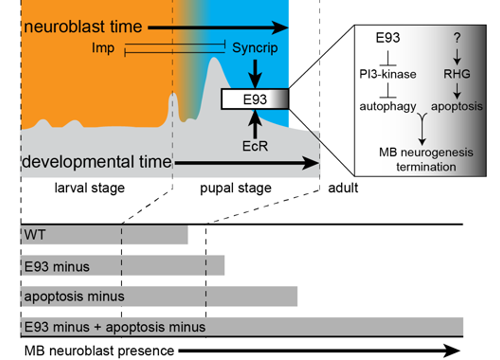
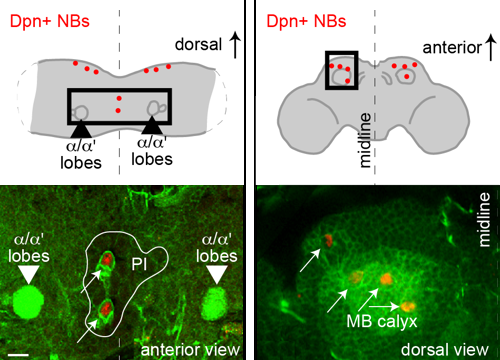
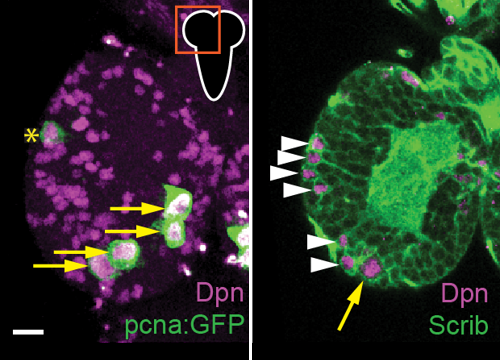
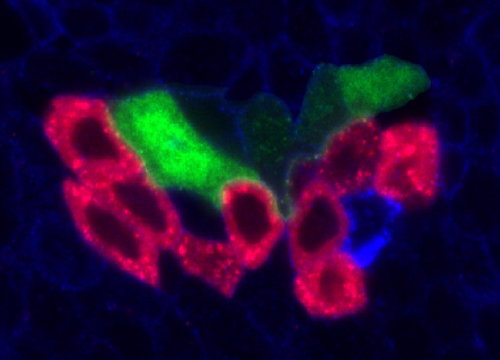
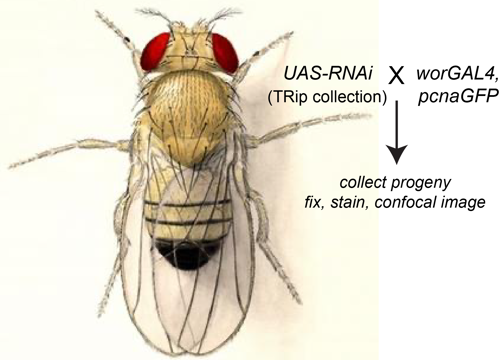
Delta controls temporal patterning
During development, neural stem cells (NSCs) divide asymmetrically, sequentially expressing a series of intrinsic factors to generate a diversity of neuron types. After cycling through temporal programs, NSCs terminally differentiate or die, bringing an end to developmental neurogenesis.
Continue Reading